- All
- Product Name
- Product Keyword
- Product Model
- Product Summary
- Product Description
- Multi Field Search
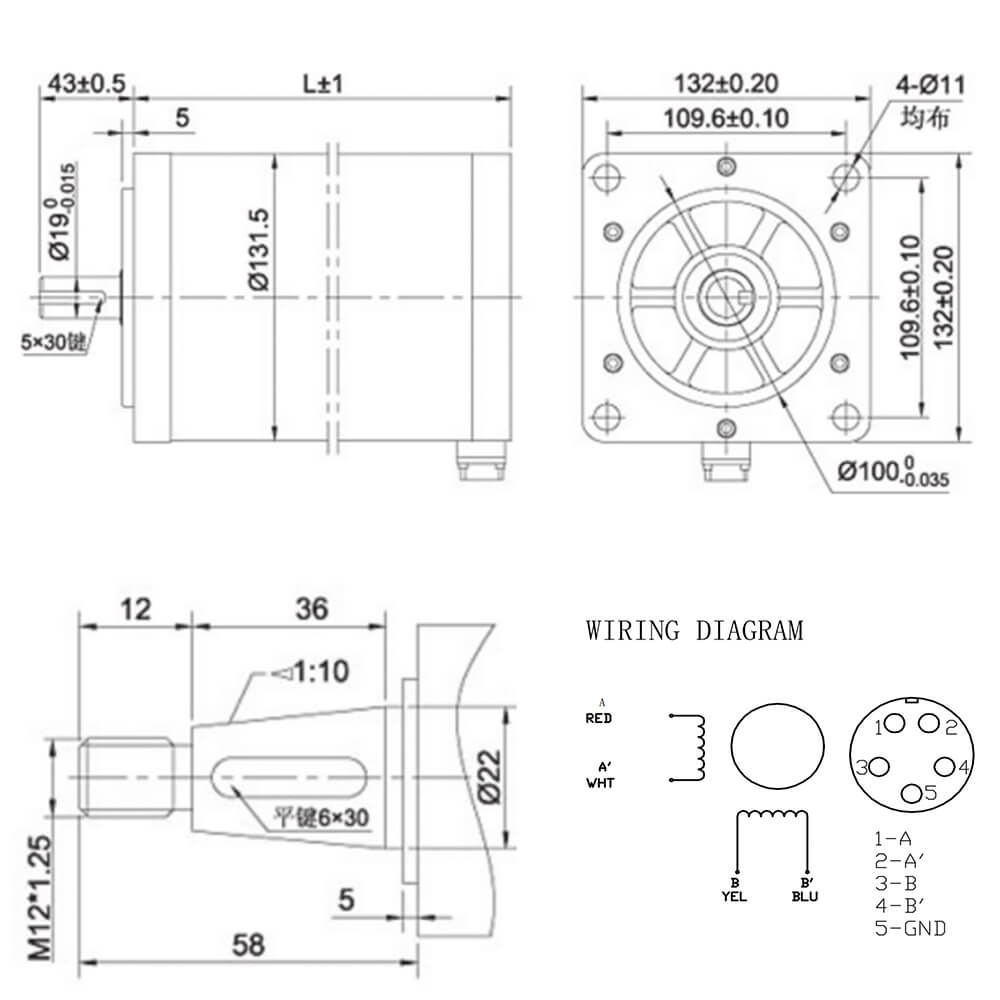
Current: 3A - 8A
Motor Length: 173mm - 285mm
Customized: Connectors, Gearbox, Encoder, Brake, Lead Screw...
| Availability: | |
|---|---|
| Quantity: | |
Nema 52 Hybrid Stepper Motor
LeanMotor
Open Loop Motors
Nema52 (130mm)
3wires, 4wires
2 Phase, 3 Phase
1.2°, 1.8°
10 Pcs
| Item | Specifications |
| Step Angle | 1.8° or 1.2° |
| Temperature Rise | 80℃max |
| Ambient Temperature | -20℃~+50℃ |
| Insulation Resistance | 100 MΩ Min. ,500VDC |
| Dielectric Strength | 1000VAC for 1minute |
| Model No. | Operating Voltage | Rated Current | Resistance | Inductance | Holding Torque | Noload Frequency | Starting Frequency | Mass | Motor Length |
| VDC | A | Ω | mH | N.m | No. | g.cm | Kg | mm | |
| LM130HS173-6004 | 80~325 | 6 | 0.75 | 12.6 | 25 | 25000 | 2300 | 13.3 | 173 |
| LM130HS229-6004 | 80~325 | 6 | 0.83 | 13.2 | 30 | 25000 | 2300 | 18 | 229 |
| LM130HS257-7004 | 80~325 | 7 | 0.73 | 11.7 | 40 | 23000 | 2200 | 19 | 257 |
| LM130HS285-7004 | 80~325 | 7 | 0.66 | 10 | 50 | 23000 | 2200 | 22.5 | 285 |
Note: Above only for representative products, products of special request can be made according to the customer request.
| Model No. | Operating Voltage | Rated Current | Resistance | Inductance | Holding Torque | Noload Frequency | Starting Frequency | Mass | Motor Length |
| VDC | A | Ω | mH | N.m | No. | g.cm | Kg | mm | |
| LM130H3P173 | 80~325 | 5 | 0.68 | 9.2 | 25 | 20000 | 2600 | 13.3 | 173 |
| LM130H3P229 | 80~325 | 5 | 0.94 | 14.8 | 30 | 20000 | 2500 | 17.8 | 229 |
| LM130H3P257 | 80~325 | 3 | 1.71 | 23.6 | 40 | 18000 | 2500 | 20 | 257 |
| LM130H3P285 | 80~325 | 6 | 1.18 | 19.4 | 50 | 18000 | 2500 | 22.5 | 285 |
Note: Above only for representative products, products of special request can be made according to the customer request.
| A+ | A- | B+ | B- |
| Black | Green | Red | Blue |
| U | V | W |
| Red | Yellow | Green |
| Item | Specifications |
| Step Angle | 1.8° or 1.2° |
| Temperature Rise | 80℃max |
| Ambient Temperature | -20℃~+50℃ |
| Insulation Resistance | 100 MΩ Min. ,500VDC |
| Dielectric Strength | 1000VAC for 1minute |
| Model No. | Operating Voltage | Rated Current | Resistance | Inductance | Holding Torque | Noload Frequency | Starting Frequency | Mass | Motor Length |
| VDC | A | Ω | mH | N.m | No. | g.cm | Kg | mm | |
| LM130HS173-6004 | 80~325 | 6 | 0.75 | 12.6 | 25 | 25000 | 2300 | 13.3 | 173 |
| LM130HS229-6004 | 80~325 | 6 | 0.83 | 13.2 | 30 | 25000 | 2300 | 18 | 229 |
| LM130HS257-7004 | 80~325 | 7 | 0.73 | 11.7 | 40 | 23000 | 2200 | 19 | 257 |
| LM130HS285-7004 | 80~325 | 7 | 0.66 | 10 | 50 | 23000 | 2200 | 22.5 | 285 |
Note: Above only for representative products, products of special request can be made according to the customer request.
| Model No. | Operating Voltage | Rated Current | Resistance | Inductance | Holding Torque | Noload Frequency | Starting Frequency | Mass | Motor Length |
| VDC | A | Ω | mH | N.m | No. | g.cm | Kg | mm | |
| LM130H3P173 | 80~325 | 5 | 0.68 | 9.2 | 25 | 20000 | 2600 | 13.3 | 173 |
| LM130H3P229 | 80~325 | 5 | 0.94 | 14.8 | 30 | 20000 | 2500 | 17.8 | 229 |
| LM130H3P257 | 80~325 | 3 | 1.71 | 23.6 | 40 | 18000 | 2500 | 20 | 257 |
| LM130H3P285 | 80~325 | 6 | 1.18 | 19.4 | 50 | 18000 | 2500 | 22.5 | 285 |
Note: Above only for representative products, products of special request can be made according to the customer request.
| A+ | A- | B+ | B- |
| Black | Green | Red | Blue |
| U | V | W |
| Red | Yellow | Green |

Connectors, Gearbox, Encoder, Brake, Integrated Driver...
Connectors, Gearbox, Encoder, Brake, Integrated Driver...
1. What is a NEMA 52 hybrid stepping motor?
A NEMA 52 hybrid stepping motor is a high-torque stepper motor with a 5.2-inch (132 mm) frame size, designed for precise positioning in industrial applications.
2. What are the main advantages of hybrid stepping motors?
Hybrid stepper motors combine the features of permanent magnet and variable reluctance motors, providing high torque, precise step accuracy, and smooth motion.
3. What torque can a NEMA 52 hybrid stepping motor deliver?
Depending on winding and motor length, it can deliver high torque suitable for heavy-load industrial applications.
4. What is the step angle of a NEMA 52 stepper motor?
Standard step angle is 1.8° per step (200 steps per revolution), with microstepping options for higher resolution.
5. Can the motor operate continuously?
Yes, designed for continuous-duty operation under proper driver control and thermal management.
6. What voltage and current ratings are available?
Voltage and current can be customized, with standard options suitable for industrial drivers and controllers.
7. What applications commonly use NEMA 52 hybrid stepping motors?
They are used in CNC machines, large automation equipment, robotics, conveyor systems, and industrial positioning applications.
8. How does a hybrid stepper motor compare to a permanent magnet stepper motor?
Hybrid motors provide higher torque, better holding torque, and improved high-speed performance compared to standard permanent magnet motors.
9. Can NEMA 52 stepper motors replace servo motors?
In medium- to high-torque applications requiring precise positioning at moderate speeds, they can serve as a cost-effective alternative.
10. How is speed controlled in a hybrid stepper motor?
Speed is controlled using compatible stepper drivers, which provide full-step, half-step, or microstepping operation.
11. Can NEMA 52 hybrid stepper motors be customized?
Yes, factories can adjust torque, winding configuration, motor length, and shaft dimensions to meet specific requirements.
12. Are different shaft types available?
Yes, options include solid shafts, D-shaped shafts, keyed shafts, or custom-machined shafts.
13. Can encoders or sensors be added?
Yes, incremental or absolute encoders can be integrated for closed-loop feedback and higher accuracy.
14. Can the motor be supplied with a matched stepper driver?
Yes, stepper drivers optimized for the motor’s current and voltage can be provided for seamless operation.
15. Are high-torque or high-speed versions available?
Yes, motor design can be tailored for higher torque or faster speed depending on application needs.
16. Can the motor be adapted for harsh environments?
Yes, IP-rated housings, corrosion-resistant coatings, and high-temperature windings are available.
17. Are geared versions of NEMA 52 hybrid stepper motors available?
Yes, planetary or spur gearboxes can be integrated for higher torque or reduced output speed.
18. What quality control tests are performed?
Testing includes torque verification, step accuracy, thermal testing, vibration analysis, and endurance testing.
19. What is the typical lead time for custom NEMA 52 motors?
Prototypes usually take 2–4 weeks, while mass production typically requires 4–8 weeks.
20. How does factory-level customization improve performance?
Customization ensures optimal matching of torque, speed, and mechanical integration, resulting in higher efficiency, accuracy, and long-term reliability.
1. What is a NEMA 52 hybrid stepping motor?
A NEMA 52 hybrid stepping motor is a high-torque stepper motor with a 5.2-inch (132 mm) frame size, designed for precise positioning in industrial applications.
2. What are the main advantages of hybrid stepping motors?
Hybrid stepper motors combine the features of permanent magnet and variable reluctance motors, providing high torque, precise step accuracy, and smooth motion.
3. What torque can a NEMA 52 hybrid stepping motor deliver?
Depending on winding and motor length, it can deliver high torque suitable for heavy-load industrial applications.
4. What is the step angle of a NEMA 52 stepper motor?
Standard step angle is 1.8° per step (200 steps per revolution), with microstepping options for higher resolution.
5. Can the motor operate continuously?
Yes, designed for continuous-duty operation under proper driver control and thermal management.
6. What voltage and current ratings are available?
Voltage and current can be customized, with standard options suitable for industrial drivers and controllers.
7. What applications commonly use NEMA 52 hybrid stepping motors?
They are used in CNC machines, large automation equipment, robotics, conveyor systems, and industrial positioning applications.
8. How does a hybrid stepper motor compare to a permanent magnet stepper motor?
Hybrid motors provide higher torque, better holding torque, and improved high-speed performance compared to standard permanent magnet motors.
9. Can NEMA 52 stepper motors replace servo motors?
In medium- to high-torque applications requiring precise positioning at moderate speeds, they can serve as a cost-effective alternative.
10. How is speed controlled in a hybrid stepper motor?
Speed is controlled using compatible stepper drivers, which provide full-step, half-step, or microstepping operation.
11. Can NEMA 52 hybrid stepper motors be customized?
Yes, factories can adjust torque, winding configuration, motor length, and shaft dimensions to meet specific requirements.
12. Are different shaft types available?
Yes, options include solid shafts, D-shaped shafts, keyed shafts, or custom-machined shafts.
13. Can encoders or sensors be added?
Yes, incremental or absolute encoders can be integrated for closed-loop feedback and higher accuracy.
14. Can the motor be supplied with a matched stepper driver?
Yes, stepper drivers optimized for the motor’s current and voltage can be provided for seamless operation.
15. Are high-torque or high-speed versions available?
Yes, motor design can be tailored for higher torque or faster speed depending on application needs.
16. Can the motor be adapted for harsh environments?
Yes, IP-rated housings, corrosion-resistant coatings, and high-temperature windings are available.
17. Are geared versions of NEMA 52 hybrid stepper motors available?
Yes, planetary or spur gearboxes can be integrated for higher torque or reduced output speed.
18. What quality control tests are performed?
Testing includes torque verification, step accuracy, thermal testing, vibration analysis, and endurance testing.
19. What is the typical lead time for custom NEMA 52 motors?
Prototypes usually take 2–4 weeks, while mass production typically requires 4–8 weeks.
20. How does factory-level customization improve performance?
Customization ensures optimal matching of torque, speed, and mechanical integration, resulting in higher efficiency, accuracy, and long-term reliability.