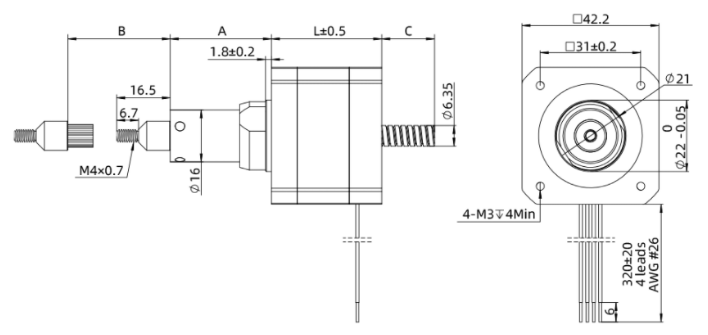
- All
- Product Name
- Product Keyword
- Product Model
- Product Summary
- Product Description
- Multi Field Search
Current: 1.33A - 1.7A
Motor Length: 34mm - 60mm
Customized: Connectors, Gearbox, Encoder, Brake, Lead Screw, Integrated Driver...
| Availability: | |
|---|---|
| Quantity: | |
Nema 17 Captive Linear Actuator Stepper Motor
LEANMOTOR
Linear Motors
Captive Linear
Nema17 (42mm)
4wires
2 Phase
1.8°
10 Pcs
General Specifications:
| Item | Specifications |
| Step Angle | 1.8° |
| Temperature Rise | 80℃max |
| Ambient Temperature | -20℃~+50℃ |
| Insulation Resistance | 100 MΩ Min. ,500VDC |
| Dielectric Strength | 500VAC for 1minute |
| Shaft Radial Play | 0.02Max. (450g-load) |
| Shaft Axial Play | 0.08Max. (450g-load) |
| Max. radial force | 28N (20mm from the flange) |
| Max. axial force | 10N |
| Model No. | Step Angle | Motor Length | Current | Resistance | Inductance | Holding Torque | # of Leads | Detent Torque | Rotor Inertia | Mass |
| ( °) | (L)mm | A | Ω | mH | Kg.cm | No. | g.cm | g.cm2 | Kg | |
| LM42HSK34-1334 | 1.8 | 34 | 1.33 | 2.1 | 2.5 | 2.6 | 4 | 120 | 34 | 0.22 |
| LM42HSK40-1704 | 1.8 | 40 | 1.7 | 1.5 | 2.3 | 4.2 | 4 | 150 | 54 | 0.28 |
| LM42HSK48-1684 | 1.8 | 48 | 1.68 | 1.65 | 2.8 | 5.5 | 4 | 260 | 68 | 0.38 |
| LM42HSK60-1704 | 1.8 | 60 | 1.7 | 3 | 6.2 | 7.3 | 4 | 280 | 102 | 0.55 |
Note: Above only for representative products, products of special request can be made according to the customer request.
| A+ | A- | B+ | B- |
| Black | Green | Red | Blue |
General Specifications:
| Item | Specifications |
| Step Angle | 1.8° |
| Temperature Rise | 80℃max |
| Ambient Temperature | -20℃~+50℃ |
| Insulation Resistance | 100 MΩ Min. ,500VDC |
| Dielectric Strength | 500VAC for 1minute |
| Shaft Radial Play | 0.02Max. (450g-load) |
| Shaft Axial Play | 0.08Max. (450g-load) |
| Max. radial force | 28N (20mm from the flange) |
| Max. axial force | 10N |
| Model No. | Step Angle | Motor Length | Current | Resistance | Inductance | Holding Torque | # of Leads | Detent Torque | Rotor Inertia | Mass |
| ( °) | (L)mm | A | Ω | mH | Kg.cm | No. | g.cm | g.cm2 | Kg | |
| LM42HSK34-1334 | 1.8 | 34 | 1.33 | 2.1 | 2.5 | 2.6 | 4 | 120 | 34 | 0.22 |
| LM42HSK40-1704 | 1.8 | 40 | 1.7 | 1.5 | 2.3 | 4.2 | 4 | 150 | 54 | 0.28 |
| LM42HSK48-1684 | 1.8 | 48 | 1.68 | 1.65 | 2.8 | 5.5 | 4 | 260 | 68 | 0.38 |
| LM42HSK60-1704 | 1.8 | 60 | 1.7 | 3 | 6.2 | 7.3 | 4 | 280 | 102 | 0.55 |
Note: Above only for representative products, products of special request can be made according to the customer request.
| A+ | A- | B+ | B- |
| Black | Green | Red | Blue |

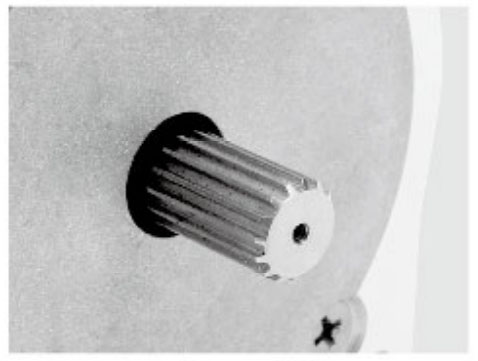
Connectors, Gearbox, Encoder, Brake, Integrated Driver...

Metal Pulleys

Plastic Pulley

Gear
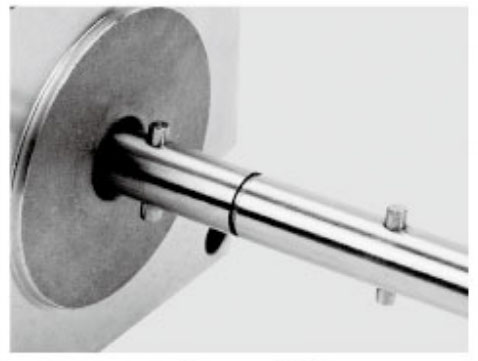
Shaft Pin

Threaded Shaft

Panel Mount
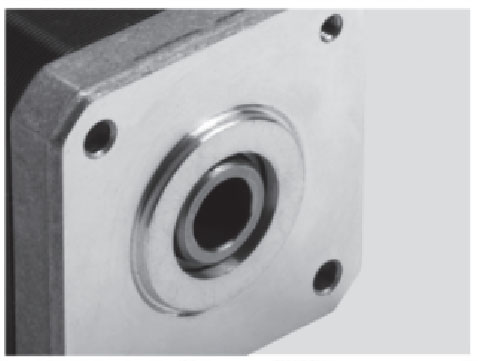
Hollow Shaft

Threaded Shaft
Panel Mount
Single Flat

Dual Flat
Key Shaft
Cables

Flanges
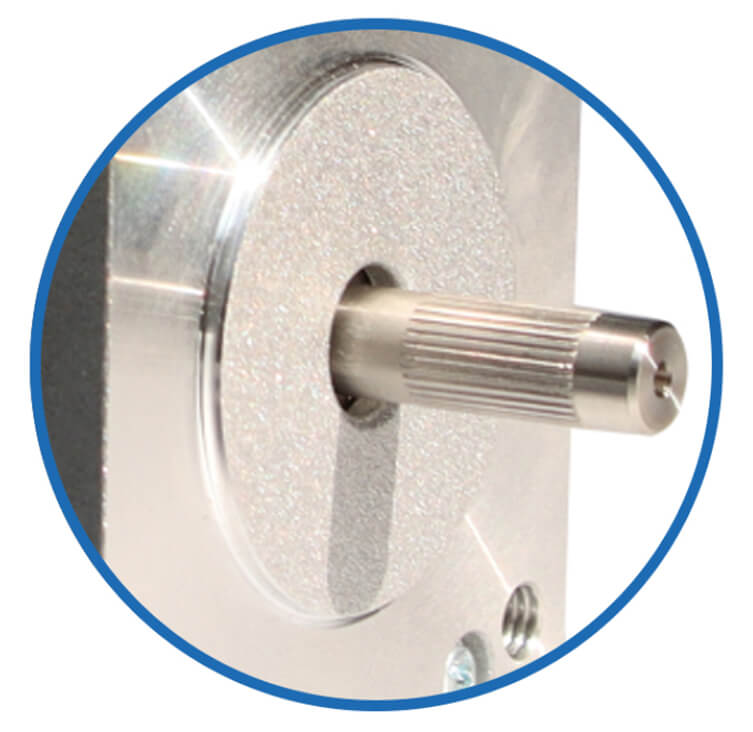

Shaft
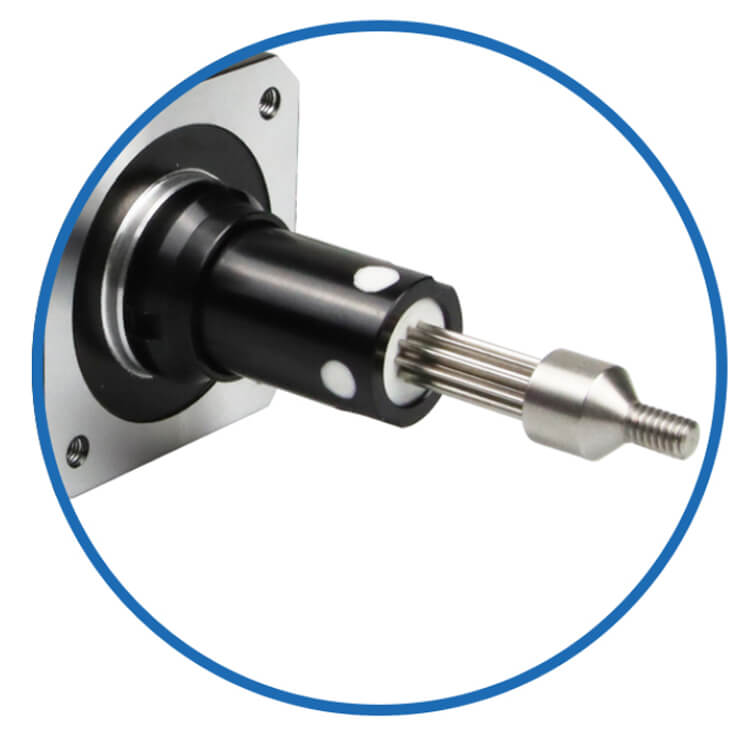

Lead Screw Rod

Encoders

Brakes
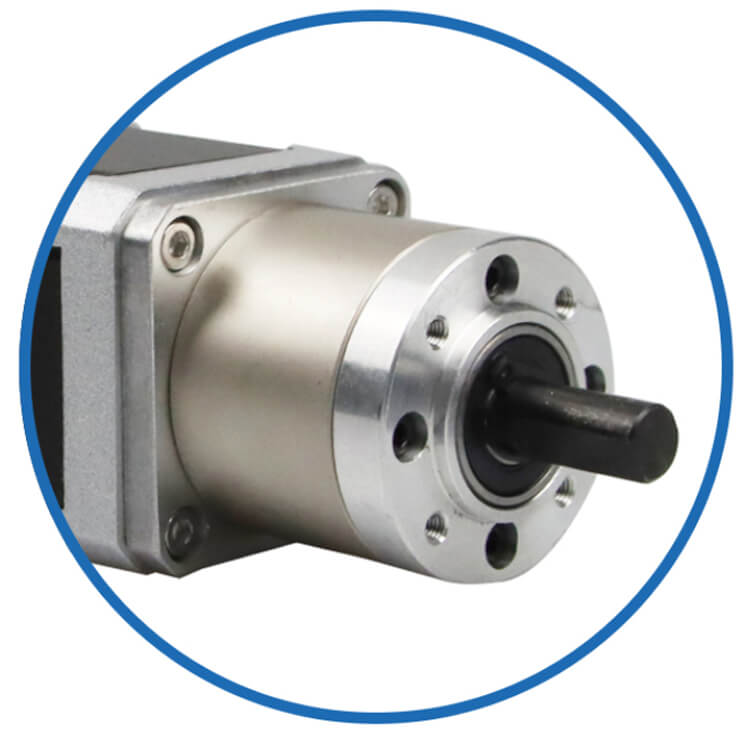

Gearboxes
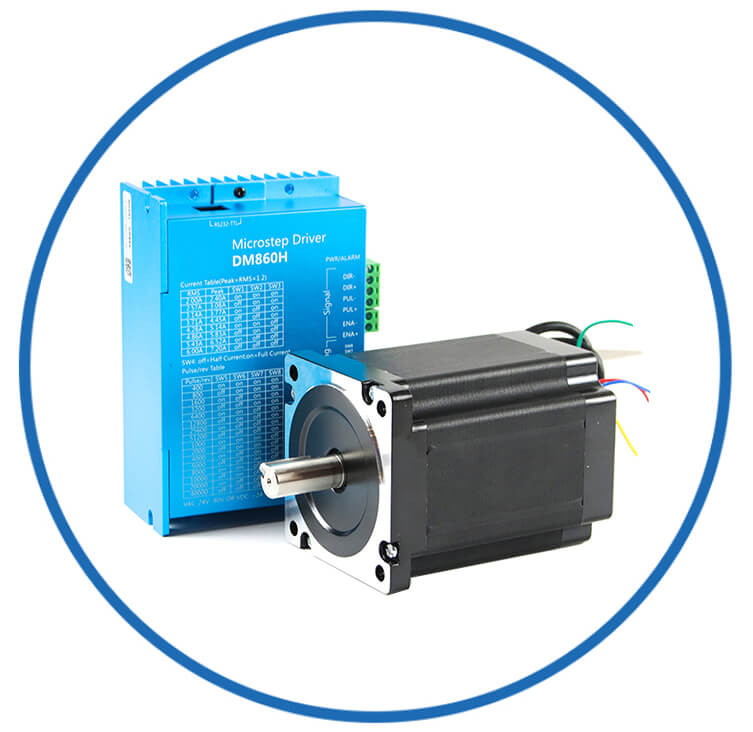

Motor Kits
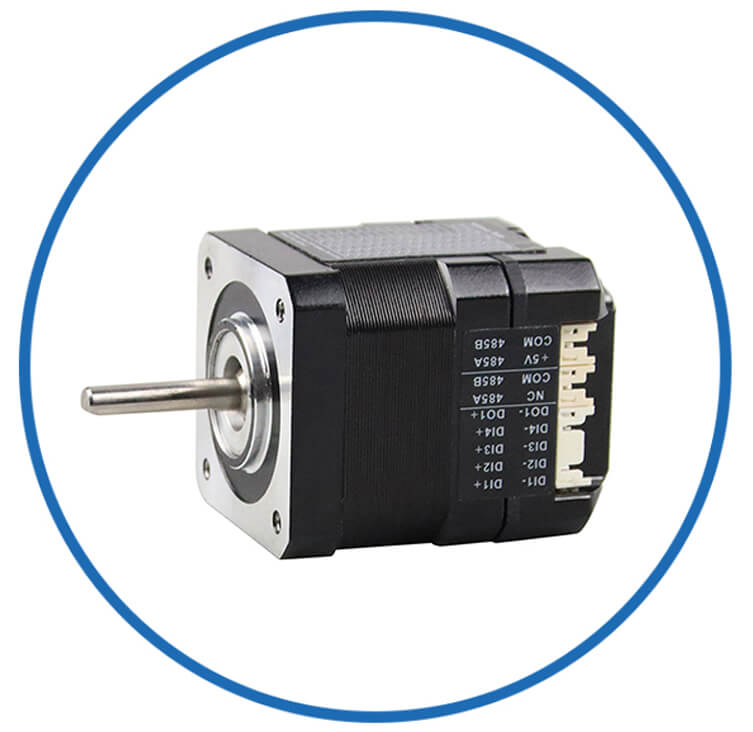

Integrated Drivers

More Customized
Connectors, Gearbox, Encoder, Brake, Integrated Driver...

Metal Pulleys

Plastic Pulley

Gear

Shaft Pin

Threaded Shaft

Panel Mount

Hollow Shaft

Threaded Shaft

Panel Mount

Single Flat

Dual Flat

Key Shaft

Cables

Flanges

Shaft

Lead Screw Rod

Encoders

Brakes

Gearboxes

Motor Kits

Integrated Drivers

More Customized
 Nema 17 42HSK Captive Linear Lead Screw Rod Dimension.png
Nema 17 42HSK Captive Linear Lead Screw Rod Dimension.png
 Nema 17 42HSK Captive Linear Lead Screw Rod Dimension.png
Nema 17 42HSK Captive Linear Lead Screw Rod Dimension.png
1. What is a NEMA 17 linear captive stepping motor?
A NEMA 17 linear captive stepper motor is a 42 mm frame stepper motor with an integrated lead screw that produces linear motion without external guides.
2. What does “captive” mean in this context?
“Captive” means the lead screw is fixed within the motor body and does not rotate freely, translating motor rotation directly into linear motion.
3. What are the main advantages of a linear captive stepper motor?
Advantages include compact size, high linear precision, low backlash, ease of installation, and minimal additional mechanical components.
4. What is the typical step angle of a NEMA 17 linear captive motor?
The standard step angle is 1.8°, and microstepping can further increase positioning resolution.
5. What lead screw pitches are available?
Various lead screw pitches can be customized to balance speed and thrust force according to the application.
6. How much linear thrust can the motor generate?
Thrust depends on motor torque and lead screw pitch, suitable for light to medium-load linear positioning applications.
7. Can this motor operate continuously?
Yes, it is designed for continuous duty with proper stepper driver control and thermal management.
8. What applications commonly use NEMA 17 linear captive motors?
Typical applications include 3D printers, lab automation, medical devices, optical instruments, and small linear actuators.
9. How does a linear captive motor compare to a rotary motor with external linear conversion?
Captive motors simplify mechanical design, reduce backlash, increase positioning accuracy, and save space compared to rotary-to-linear setups.
10. Are these motors suitable for high-speed applications?
Yes, but linear speed is limited by the lead screw pitch and microstepping configuration; designed primarily for precision rather than ultra-high speed.
11. Can NEMA 17 linear captive motors be customized?
Yes, manufacturers can customize motor length, lead screw pitch, voltage, current, and torque.
12. Are different lead screw materials available?
Yes, lead screws can be stainless steel or other corrosion-resistant materials.
13. Can the nut design be customized?
Yes, options include standard nuts, anti-backlash nuts, or specialized wear-resistant designs.
14. Can encoders or sensors be added?
Yes, incremental or absolute encoders can be integrated for closed-loop position control.
15. Can the motor be supplied with a matching stepper driver?
Yes, compatible stepper drivers can be provided to optimize performance.
16. Are low-noise or low-vibration versions available?
Yes, optimized windings, precision lead screws, and microstepping help reduce noise and vibration.
17. Can the motor be adapted for harsh environments?
Yes, IP-rated protection, special coatings, or high-temperature insulation can be applied.
18. Can shaft length and mounting options be customized?
Yes, stroke length, mounting holes, and mechanical interfaces can be tailored to specific applications.
19. What quality control tests are performed before shipment?
Testing includes step accuracy, thrust testing, insulation and resistance tests, and long-term durability verification.
20. How does factory-level customization improve system performance?
Customization ensures optimal matching of linear speed, thrust, stroke, and electrical characteristics for enhanced reliability, precision, and service life.
1. What is a NEMA 17 linear captive stepping motor?
A NEMA 17 linear captive stepper motor is a 42 mm frame stepper motor with an integrated lead screw that produces linear motion without external guides.
2. What does “captive” mean in this context?
“Captive” means the lead screw is fixed within the motor body and does not rotate freely, translating motor rotation directly into linear motion.
3. What are the main advantages of a linear captive stepper motor?
Advantages include compact size, high linear precision, low backlash, ease of installation, and minimal additional mechanical components.
4. What is the typical step angle of a NEMA 17 linear captive motor?
The standard step angle is 1.8°, and microstepping can further increase positioning resolution.
5. What lead screw pitches are available?
Various lead screw pitches can be customized to balance speed and thrust force according to the application.
6. How much linear thrust can the motor generate?
Thrust depends on motor torque and lead screw pitch, suitable for light to medium-load linear positioning applications.
7. Can this motor operate continuously?
Yes, it is designed for continuous duty with proper stepper driver control and thermal management.
8. What applications commonly use NEMA 17 linear captive motors?
Typical applications include 3D printers, lab automation, medical devices, optical instruments, and small linear actuators.
9. How does a linear captive motor compare to a rotary motor with external linear conversion?
Captive motors simplify mechanical design, reduce backlash, increase positioning accuracy, and save space compared to rotary-to-linear setups.
10. Are these motors suitable for high-speed applications?
Yes, but linear speed is limited by the lead screw pitch and microstepping configuration; designed primarily for precision rather than ultra-high speed.
11. Can NEMA 17 linear captive motors be customized?
Yes, manufacturers can customize motor length, lead screw pitch, voltage, current, and torque.
12. Are different lead screw materials available?
Yes, lead screws can be stainless steel or other corrosion-resistant materials.
13. Can the nut design be customized?
Yes, options include standard nuts, anti-backlash nuts, or specialized wear-resistant designs.
14. Can encoders or sensors be added?
Yes, incremental or absolute encoders can be integrated for closed-loop position control.
15. Can the motor be supplied with a matching stepper driver?
Yes, compatible stepper drivers can be provided to optimize performance.
16. Are low-noise or low-vibration versions available?
Yes, optimized windings, precision lead screws, and microstepping help reduce noise and vibration.
17. Can the motor be adapted for harsh environments?
Yes, IP-rated protection, special coatings, or high-temperature insulation can be applied.
18. Can shaft length and mounting options be customized?
Yes, stroke length, mounting holes, and mechanical interfaces can be tailored to specific applications.
19. What quality control tests are performed before shipment?
Testing includes step accuracy, thrust testing, insulation and resistance tests, and long-term durability verification.
20. How does factory-level customization improve system performance?
Customization ensures optimal matching of linear speed, thrust, stroke, and electrical characteristics for enhanced reliability, precision, and service life.