- All
- Product Name
- Product Keyword
- Product Model
- Product Summary
- Product Description
- Multi Field Search
| Availability: | |
|---|---|
| Quantity: | |
LMBLD300 V2
LeanMotor
10 Pcs
LMBLD300 V2 brushless DC driver is suitable for speed regulation of three-phase brushless DC motors with power below 300W, and it can provide external potentiometer speed regulation, external analog voltage speed regulation, and upper computer (PLC, microcontroller, etc.) PWM speed regulation. At the same time the driver has a large torque start, fast start and braking, forward and reverse switching, manual and automatic speed control. It is suitable for DC brushless motors with voltage from 14V to 56V and power less than 300W.
Acc/Dec time setting
Alarm indication
Pole-pairs selection
Built-in RV Speed setting
Open/closed loop control
External potentiometer speed setting
Max output current P-sv setting
External analog signal speed setting
Motor stall torque maintenance
PWM speed setting
Restart
LMBLD300 V2 brushless DC driver is suitable for speed regulation of three-phase brushless DC motors with power below 300W, and it can provide external potentiometer speed regulation, external analog voltage speed regulation, and upper computer (PLC, microcontroller, etc.) PWM speed regulation. At the same time the driver has a large torque start, fast start and braking, forward and reverse switching, manual and automatic speed control. It is suitable for DC brushless motors with voltage from 14V to 56V and power less than 300W.
Acc/Dec time setting
Alarm indication
Pole-pairs selection
Built-in RV Speed setting
Open/closed loop control
External potentiometer speed setting
Max output current P-sv setting
External analog signal speed setting
Motor stall torque maintenance
PWM speed setting
Restart
| Brand | Leanmotor |
| Model | LMBLD300 V2 |
| Driver Type | DC Brushless Motor Driver |
| DC / AC | DC |
| Suitable Motor | 3-Phase DC Brushless motor |
| Input Voltage | 14VDC - 56VDC |
| Output Current | Max 15A |
| Hall signal voltage | 5V |
| Hall drive current | 12mA |
| Motor speed range | 0rpm - 20000rpm |
| External potentiometer | 10kΩ |
| Control method | Open and closed loop control |
| JKBLD300 DC brushless driver is suitable for speed regulation of three-phase DC brushless motors with power below 300W, and it can provide external potentiometer speed regulation, external analog voltage speed regulation, and PWM speed regulation of upper computer (PLC, microcontroller, etc.), etc. At the same time, the driver has large torque starting, fast starting and braking, forward and reverse switching, and manual and automatic speed regulation. At the same time the driver has a large torque start, fast start and braking, forward and reverse switching, manual and automatic speed control. It is suitable for DC brushless motors with voltage from 14V to 56V and power less than 300W. | |
| Parameter | Min | Typical | Max | Unit |
| Voltage Input DC | 14 | 48 | 56 | V |
| Output current | - | - | 15 | A |
| Motor speed range | 0 | - | 20000 | RPM |
| Hall signal voltage | - | - | 5 | V |
| Hall drive current | 12 | - | - | MA |
| External potentiometer | - | 10 | - | KΩ |
| Heat Sinking Method | Natural cooling or fan-forced cooling |
| Atmosphere | Avoid dust, oil stains, and corrosive gases |
| Operating Temperature | +10℃ ~ +50℃ |
| Ambient Humidity | 90% RH (non-condensing) |
| Vibration Resistance | 5.9m/s² maximum |
| Storage Temperature | 0℃ ~ +50℃ |
| Signal category | Terminal | Functional Description |
| Control signal | BRK | When the BRK terminal and COM terminal are disconnected or high-level input, the motor brake stops, and when short circuited or low-level input, the motor runs. |
| EN | When the EN terminal and COM terminal are disconnected or high-level input, the motor slowly stops, and when short circuited or low-level input, the motor runs. | |
| F/R | When the F/R terminal and COM terminal are disconnected or high-level input, the motor rotates forward, and when short circuited or low-level input, the motor reverses. | |
| COM | Common port (OV reference level). | |
| SV | ① External potentiometer speed setting input; ② External analog voltage input terminal ③ PWM speed setting input | |
| Hall signal | REF+ | DC brushless motor Hall signal grounded. |
| HU | DC brushless motor Hall signal HU. | |
| HV | DC brushless motor Hall signal HV. | |
| HW | DC brushless motor Hall signal HW. | |
| REF- | DC brushless motor Hall signal grounded. | |
| Motor connection | W | Motor line W phase |
| V | Motor line V phase | |
| U | Motor line U phase | |
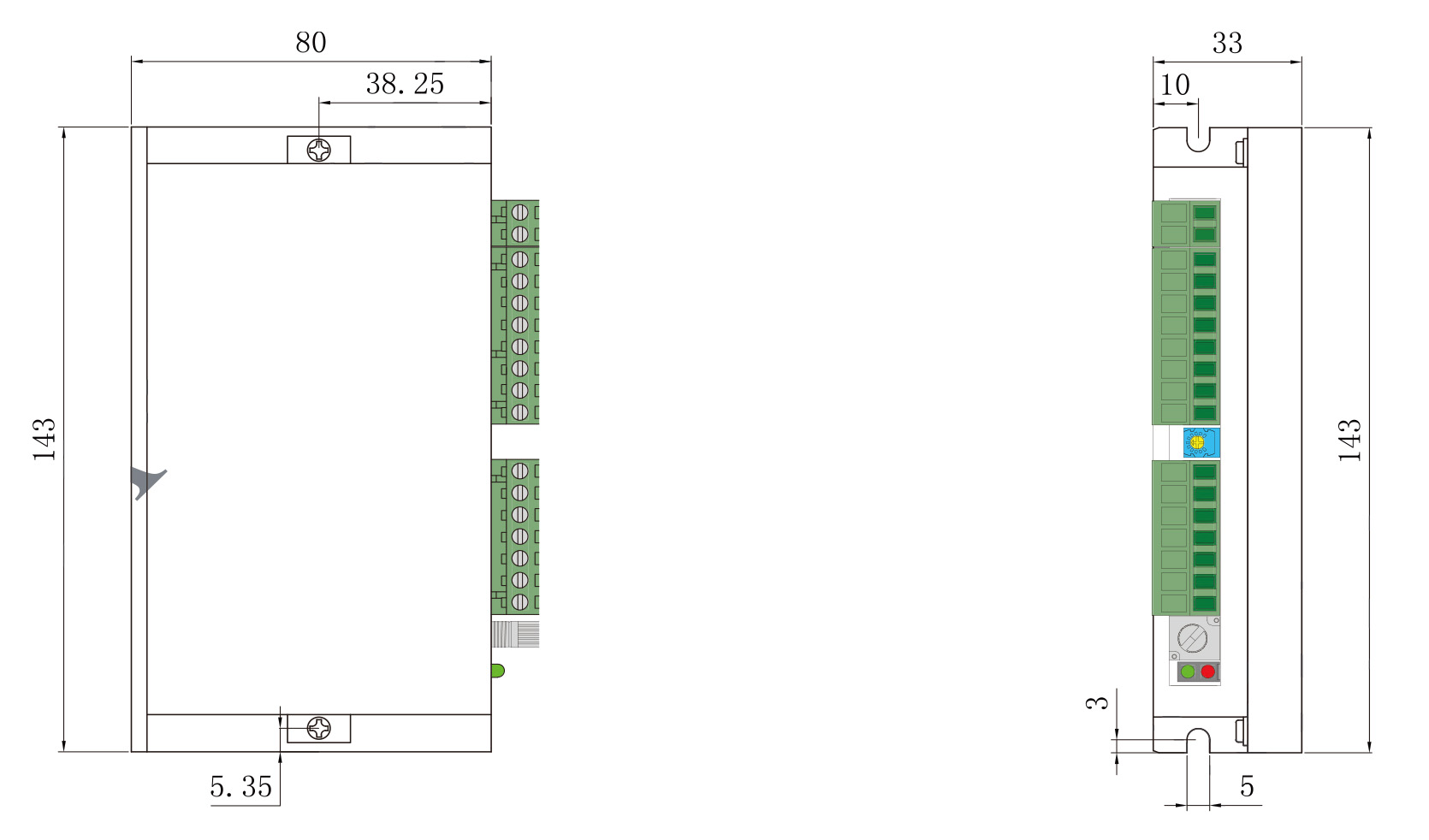
Power connection | DC+ | Power supply positive electrode (12-30VDC) |
| DC- | Power supply negative electrode | |
Output signal | SPEED | Output a pulse frequency that matches the operating speed of the motor. The motor speed can be calculated using SPEED-OUT. The calculation formula is: N (rpm)=(F/P) × 60/3 F: Output pulse frequency (Hz); P: Number of motor poles; N: Motor speed |
| ALM | The output signal of the motor or drive control fault signal is normally 5V, and in the event of a fault, it is 0V. |
| Brand | Leanmotor |
| Model | LMBLD300 V2 |
| Driver Type | DC Brushless Motor Driver |
| DC / AC | DC |
| Suitable Motor | 3-Phase DC Brushless motor |
| Input Voltage | 14VDC - 56VDC |
| Output Current | Max 15A |
| Hall signal voltage | 5V |
| Hall drive current | 12mA |
| Motor speed range | 0rpm - 20000rpm |
| External potentiometer | 10kΩ |
| Control method | Open and closed loop control |
| JKBLD300 DC brushless driver is suitable for speed regulation of three-phase DC brushless motors with power below 300W, and it can provide external potentiometer speed regulation, external analog voltage speed regulation, and PWM speed regulation of upper computer (PLC, microcontroller, etc.), etc. At the same time, the driver has large torque starting, fast starting and braking, forward and reverse switching, and manual and automatic speed regulation. At the same time the driver has a large torque start, fast start and braking, forward and reverse switching, manual and automatic speed control. It is suitable for DC brushless motors with voltage from 14V to 56V and power less than 300W. | |
| Parameter | Min | Typical | Max | Unit |
| Voltage Input DC | 14 | 48 | 56 | V |
| Output current | - | - | 15 | A |
| Motor speed range | 0 | - | 20000 | RPM |
| Hall signal voltage | - | - | 5 | V |
| Hall drive current | 12 | - | - | MA |
| External potentiometer | - | 10 | - | KΩ |
| Heat Sinking Method | Natural cooling or fan-forced cooling |
| Atmosphere | Avoid dust, oil stains, and corrosive gases |
| Operating Temperature | +10℃ ~ +50℃ |
| Ambient Humidity | 90% RH (non-condensing) |
| Vibration Resistance | 5.9m/s² maximum |
| Storage Temperature | 0℃ ~ +50℃ |
| Signal category | Terminal | Functional Description |
| Control signal | BRK | When the BRK terminal and COM terminal are disconnected or high-level input, the motor brake stops, and when short circuited or low-level input, the motor runs. |
| EN | When the EN terminal and COM terminal are disconnected or high-level input, the motor slowly stops, and when short circuited or low-level input, the motor runs. | |
| F/R | When the F/R terminal and COM terminal are disconnected or high-level input, the motor rotates forward, and when short circuited or low-level input, the motor reverses. | |
| COM | Common port (OV reference level). | |
| SV | ① External potentiometer speed setting input; ② External analog voltage input terminal ③ PWM speed setting input | |
| Hall signal | REF+ | DC brushless motor Hall signal grounded. |
| HU | DC brushless motor Hall signal HU. | |
| HV | DC brushless motor Hall signal HV. | |
| HW | DC brushless motor Hall signal HW. | |
| REF- | DC brushless motor Hall signal grounded. | |
| Motor connection | W | Motor line W phase |
| V | Motor line V phase | |
| U | Motor line U phase | |
Power connection | DC+ | Power supply positive electrode (12-30VDC) |
| DC- | Power supply negative electrode | |
Output signal | SPEED | Output a pulse frequency that matches the operating speed of the motor. The motor speed can be calculated using SPEED-OUT. The calculation formula is: N (rpm)=(F/P) × 60/3 F: Output pulse frequency (Hz); P: Number of motor poles; N: Motor speed |
| ALM | The output signal of the motor or drive control fault signal is normally 5V, and in the event of a fault, it is 0V. |

1, Q: The motor does not turn and no holding torque:
A: ① check whether the power line is connected to the wrong voltage is too low, need to increase the voltage or correct the power line
② check whether the motor wiring is correct, if not correct motor wiring. Check if the motor wiring is correct, if not, correct the motor wiring.
③ Whether the enable signal is valid, resulting in the motor does not work.
④ Is the subdividing parameter correct?
⑤ Is the current parameter correct?
2、Q:Motor does not rotate but has holding torque:
A: ① The phase sequence of motor wires is wrong, need to swap any two wires.
② Pulse signal input is wrong, need to check the pulse wiring.
3、Q: The motor torque is too small:
A: ① Phase current setting is too small, need to set the phase current corresponding to the motor.
② acceleration is too fast, reduce the acceleration value
③ motor blocking, need to rule out mechanical problems
④ drive and motor mismatch, need to replace the appropriate drive
4、Q:Motor steering error:
A: ① motor line phase sequence is wrong, need to swap any two wires
② motor line has a broken circuit, check and connect the right
5、Q:The alarm indicator light is on:
A: ① Is the motor wire connected incorrectly
② Whether there is over-voltage and under-voltage conditions
③ Motor or driver is damaged
6、Q:Motor acceleration blocking:
A: ① short acceleration time
② motor torque is too small
③ Low voltage or current
1, Q: The motor does not turn and no holding torque:
A: ① check whether the power line is connected to the wrong voltage is too low, need to increase the voltage or correct the power line
② check whether the motor wiring is correct, if not correct motor wiring. Check if the motor wiring is correct, if not, correct the motor wiring.
③ Whether the enable signal is valid, resulting in the motor does not work.
④ Is the subdividing parameter correct?
⑤ Is the current parameter correct?
2、Q:Motor does not rotate but has holding torque:
A: ① The phase sequence of motor wires is wrong, need to swap any two wires.
② Pulse signal input is wrong, need to check the pulse wiring.
3、Q: The motor torque is too small:
A: ① Phase current setting is too small, need to set the phase current corresponding to the motor.
② acceleration is too fast, reduce the acceleration value
③ motor blocking, need to rule out mechanical problems
④ drive and motor mismatch, need to replace the appropriate drive
4、Q:Motor steering error:
A: ① motor line phase sequence is wrong, need to swap any two wires
② motor line has a broken circuit, check and connect the right
5、Q:The alarm indicator light is on:
A: ① Is the motor wire connected incorrectly
② Whether there is over-voltage and under-voltage conditions
③ Motor or driver is damaged
6、Q:Motor acceleration blocking:
A: ① short acceleration time
② motor torque is too small
③ Low voltage or current